Research & Publications
The Therapeutic Market Behind Ketamir-2
Ketamir-2 (“Ketamir”) is an innovative ketamine analog with improved oral bioavailability and safety profile currently under investigation for the potential to treat neuropathic pain and to deliver ultra-rapid antidepressant effects.
Read Our Latest Article
KETAMIR-2, a new molecular entity and novel ketamine analog

Neuropathic Pain
- Neuropathic Pain is a complex pain condition that arises from dysfunction or damage to the nervous system. It is a pain state that can continue even when the initial cause of the pain, such as an injury or disease, has healed or been treated. It represents a malfunction in the nerve’s signaling rather than a response to continued harm.
- Affecting approximately 7-10% of the general population1. Examples include diabetic peripheral neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and multiple sclerosis related neuropathy.
- Existing treatments may involve medications like anticonvulsants, which can reduce the excitability of nerves, thereby dampening abnormal electrical activity, or antidepressants, which increase serotonin and norepinephrine levels that modulate the way the brain perceives pain. However, their effectiveness can be limited, and they might carry side effects. Opiates are used less frequently due to addiction risks.
- Developing targeted and efficient therapies for neuropathic pain stands as a priority for numerous pharmaceutical companies to address this common source of suffering and morbidity for treatment-resistant cases. Innovative strategies, including cannabinoid therapies, are under exploration to tackle the distinctive challenges posed by this type of pain.

Depression
- Depression encompasses various forms, including Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), which affects mood, cognition, and daily functioning; Major Depressive Disorder with Suicidal Ideation (MDD-SI), where individuals with MDD experience thoughts of suicide; and Treatment-Resistant Depression (TRD), where patients fail to respond to multiple standard therapies.
- Designed to address the challenges presented by major depressive disorder (MDD), which affects over 264 million individuals globally and poses substantial economic and societal burdens.
- Approximately 17.6M Americans are diagnosed with Major Depressive Disorder, of which 5.5M report suicidal ideation of any kind, and ~2M report suicidal ideation with intent
- Ketamir-2 is under investigation to potentially deliver ultra-rapid antidepressant effects as early as four hours after dosing.
- Hecke, et al. Neuropathic pain in the general population: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain. 2014 Apr;155(4):654-662. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.11.013.
- Anxiety Disorders | NAMI: National Alliance on Mental Illness
- Anxiety Disorders Facts and Statistics | The Recovery Village Drug and Alcohol Rehab
- SSRIs – Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; SNRIs – Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, TCAs – Tricyclic antidepressants
Superior Bioavailability
Oral bioavailability is predicted to be 80% based on a model of intestinal absorption and metabolism, more than double that of oral or intranasal absorption of ketamine, promising a potential shift to observed oral, home administration, granting patients greater autonomy, convenience, and accessibility to a potentially effective depression treatment

InSilico Analysis
The analysis highlights Ketamir and ketamine’s key receptor targets and effects. For Ketamir, BRD4 antagonists may reduce neuroinflammation and boost neuroplasticity. Ketamine’s targets, like the Alpha-2a adrenergic receptor, link to sedation and hypertension, while the Mu opioid receptor relates to addiction, and the Serotonin 5-HT2b receptor to dissociation and psychosis. It also lists reasons for REMS, including sedation, hypertension, addiction, and dissociation.

The Chung Model of Neuropathic Pain in a Rat
Surgical Procedure:
The Chung model involves tightly ligating of two (L5 and L6) segmental spinal nerves in rats. This procedure creates a partial nerve injury that mimics neuropathic pain conditions.
Behavioral Outcomes:
Following the spinal nerve ligation, rats exhibit long-lasting behavioral signs indicative of neuropathic pain, including mechanical allodynia. Response to Von Frey Filaments is measured at 14 and 21 days after the operation.
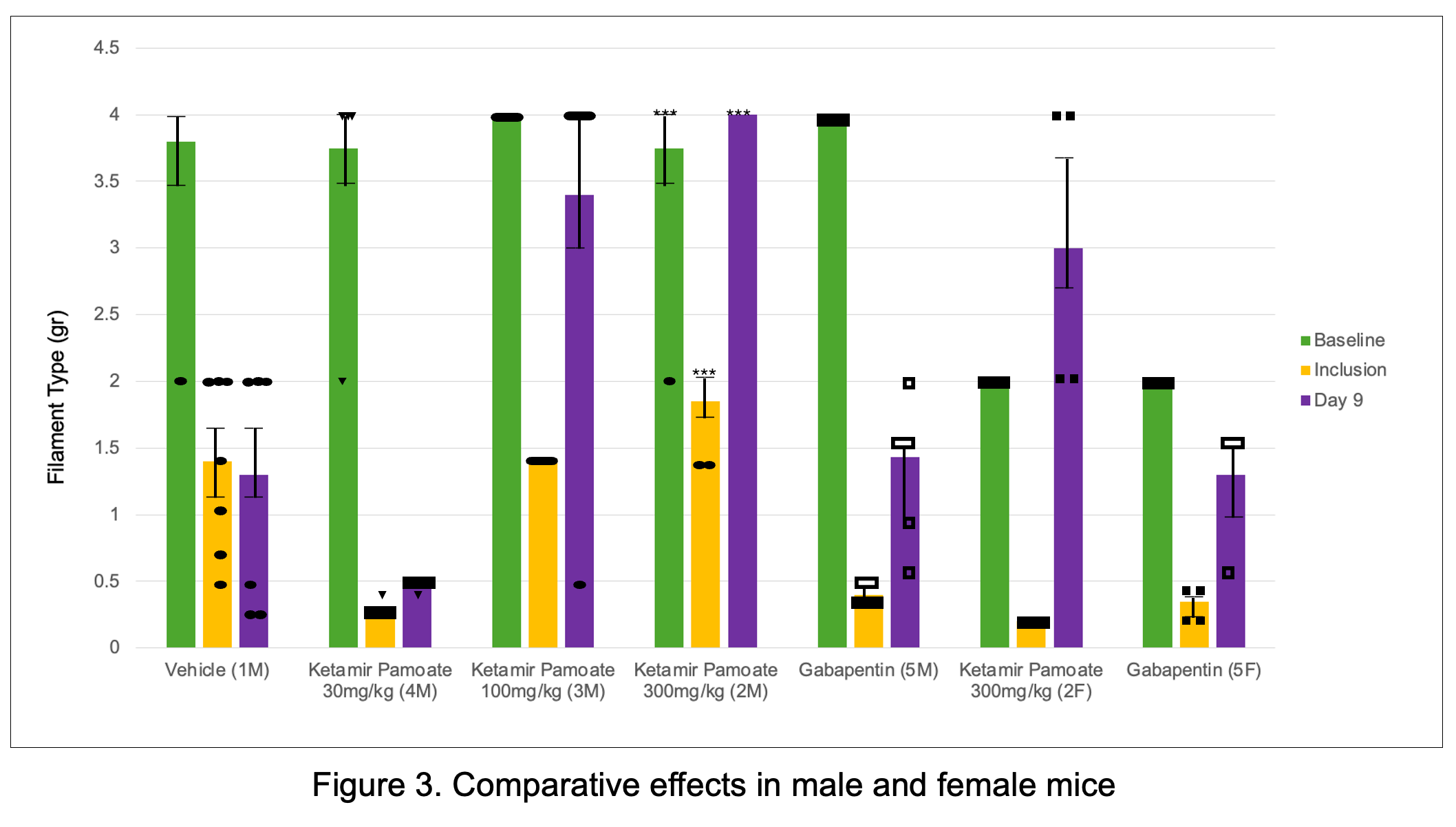
Comparative effects of several oral doses of Ketamir-2 to Ketamine, Pregabalin and Gabapentin in the Chung model of Neuropathic pain in rats
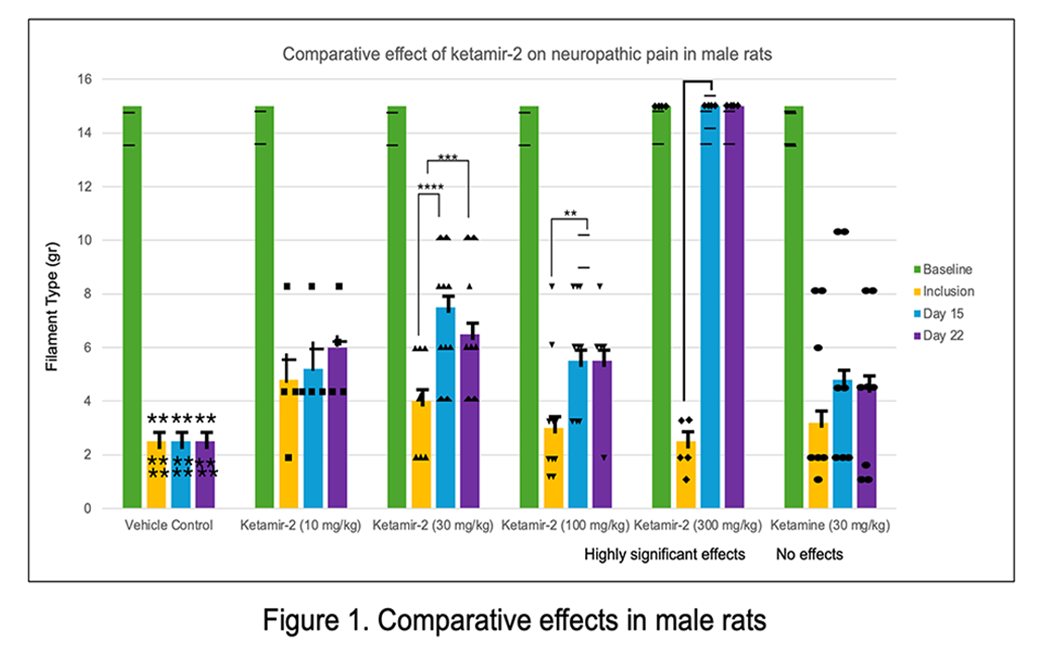

Comparative effects of several oral doses of Ketamir-2 to Ketamine in the Chung model of Neuropathic pain
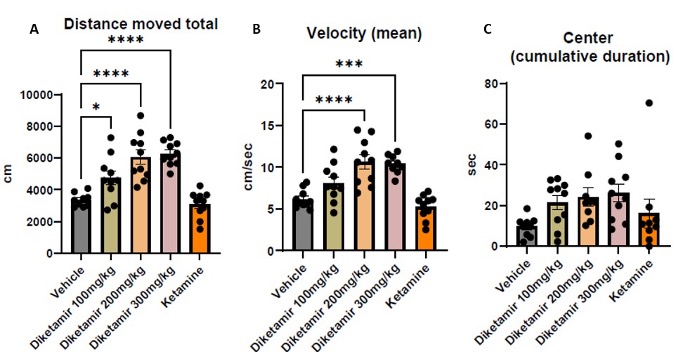
Open Field Test
The open field test is a commonly employed behavioral assays used to evaluate the efficacy of anxiety and depression medications.
Mice treated with antidepressants typically exhibit greater locomotor activity, moving more extensively and exploring a larger area of the open field compared to control mice. These treated mice are also more inclined to spend time in the central region of the open field, which indicates a decrease in anxiety and an increase in exploratory tendencies.
Mice treated with all tested concentrations of Diketamir-2 moved larger distance than vehicle treated mice. They also significantly were faster, with higher velocity compared to control. Mice treated with Diketamir also showed a trend of more time spent in the center.

Forced Swim Test
In the forced swimming test (FST), mice treated with antidepressants are generally more mobile. They also show reduced immobility time compared to control mice. Instead of remaining immobile, they exhibit increased active behaviors such as swimming and climbing. This increased activity is interpreted as a sign of decreased behavioral despair and an antidepressant-like effect.
Mice treated with Diketamir-2 show reduction in traveled distance and lower velocity. When mobility state was analyzed, 300mg/kg of Diketamir is the only Diketamir treatment that reduced hyper-mobility, and increased mobility significantly. No treatment significantly induced immobility compared to vehicle treated, however-100 and 200mg/kg Diketamir and Ketamine showed a trend of reduced immobility.
Elevated Plus Maze
In the elevated plus maze mice treated with antidepressants typically demonstrate increased exploratory behavior and reduced anxiety. These mice are more likely to enter and spend more time in the open arms of the maze, areas that anxious animals usually avoid. This increased presence in the open arms suggests an anxiolytic effect and enhanced willingness to explore novel environments.
Mice treated with Diketamir-2 moved larger distance than vehicle treated mice. They were also significantly were faster, with higher velocity, and spent more time in the center of the maze, compared to control.

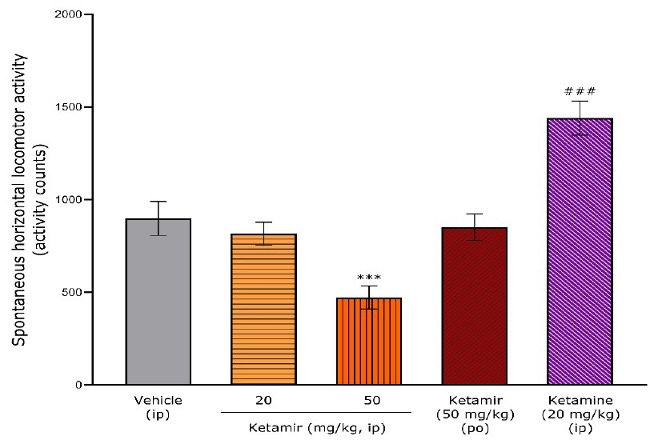
Spontaneous hyperlocomotion
Ketamine-induced hyperlocomotion is considered a schizophrenia-like effect because it models the hyperactive and psychotic symptoms observed in schizophrenia patients.
Unlike Ketamine, which resulted in marked and significant hyperlocomotion, Ketamir-2 did not produce incidences of inducing hyperlocomotion, schizophrenia-like behaviors in animal models, indicating a safer profile for patients, especially those with a predisposition to psychotic disorders.
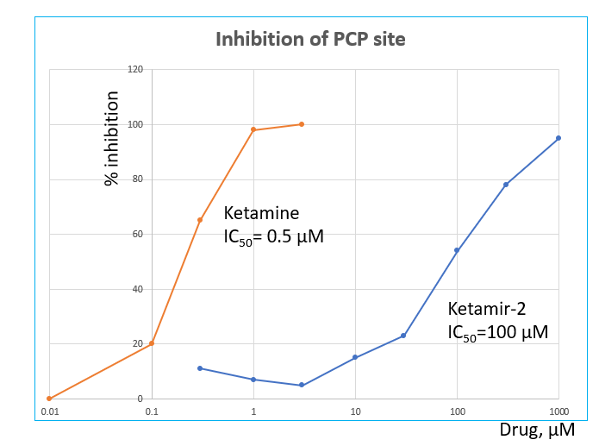
MOA
Ketamir was evaluated on a large array of receptors, transporters and binding sites. It was found that Ketamir is a low affinity NMDA receptor antagonist, that selectively binds to the PCP-site. Its IC50 on this receptor site is ~100 µM.
While Ketamine is known to also interact with several neurotransmitter transporters, including the serotonin transporter (SERT) and norepinephrine transporter (NET) and to additional sites at the NMDA-receptor complex, Ketamir-2 does not bind to the AMPA, Kainate, sigma, glutamate or to the glycine ion sites.